Maestro 3D Easy Dental Scan - Instrukcja obsługi
Wprowadzenie do instrukcji użytkownika Maestro 3D Easy Dental Scan
Celem dokumentu jest zaznajomienie użytkownika z oprogrmaowaniem Dental Easy Scan w możliwie prosty i szybki sposób.Proszę zapoznać się z instrukcją przed pierwszym uruchomieniem oprogramowania. Maestro Easy Dental Scan jest oprogramowaniem przeznaczonym do współpracy z Maestro3D dental scanners. Oprogramowanie umożliwia automatyczne skanowanie obiektów dentystycznych za pomocą jednej komendy i tworzenie obiektów 3D w pełni zautomatyzowanym procesie. Nowoczesne rozwiązania dotyczace renderingu zawarte w oporgramowaniu gwarantują wyjątkowa wydajność w pozyskiwaniu i obróbce cyfrowych obiektów.
Montaż i podłączenia
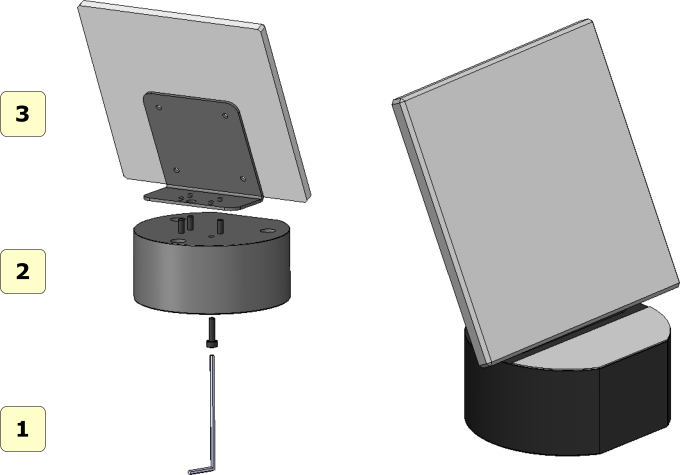
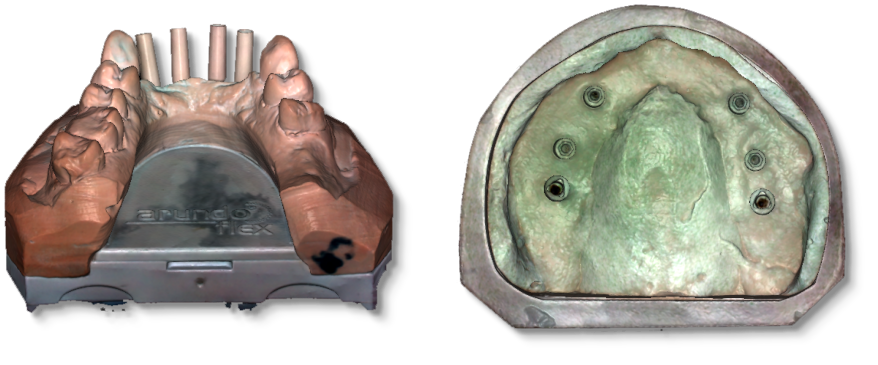
Montaż zestawu do kalibracji
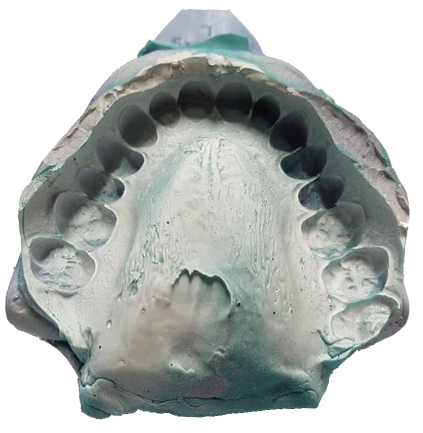
Zestaw do klaibracji powinien być zmontowany po wyjeciu z opakowania jak pokazano poniżej.
- 1 allen key;
- 2 plate;
- 3 calibration plate;
Simply screw the 4 supplied screws to join the plate to the calibration plate. Be careful not to scratch or stain the calibration plate. It is advisable to handle the plate with gloves so as not to dirty it or leave fingerprints on it.
|
WARNING
|
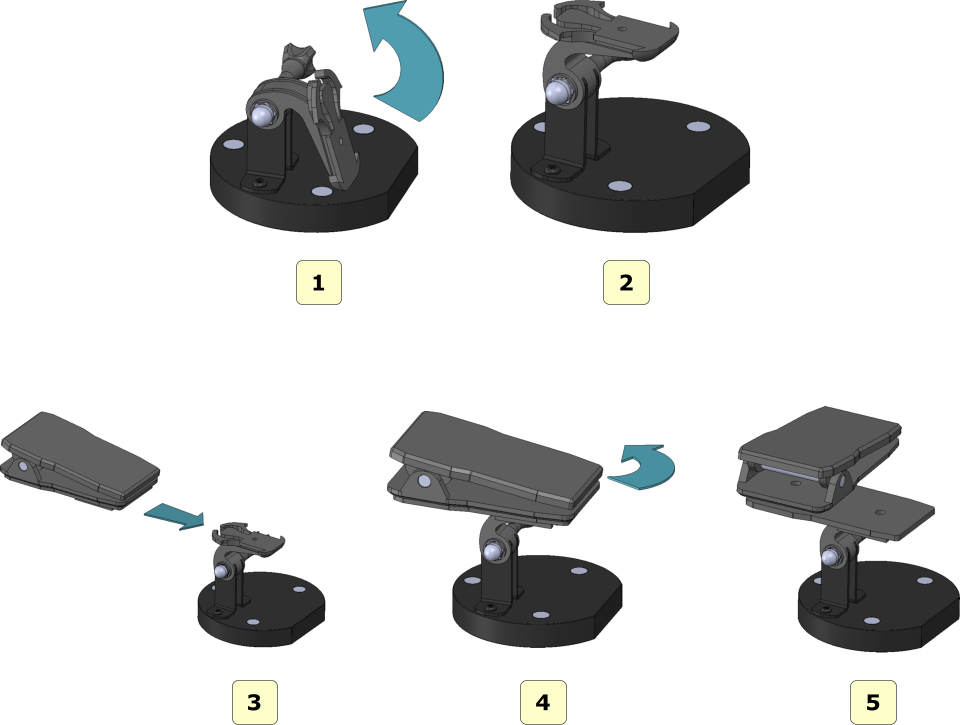
Assembly of the impression plate
See the figure below showing how the impression plate should be assembled once it has been extracted from its packaging.
Follow the steps as shown in the figure to correctly assemble the impression plate.
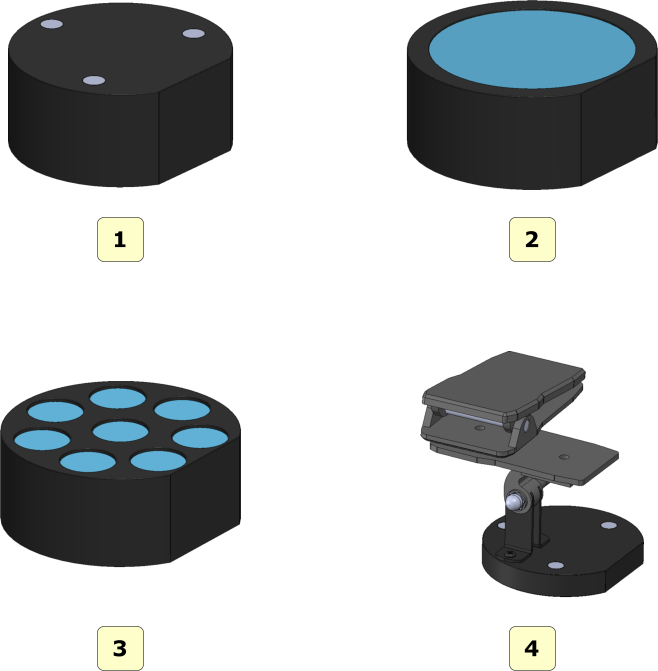
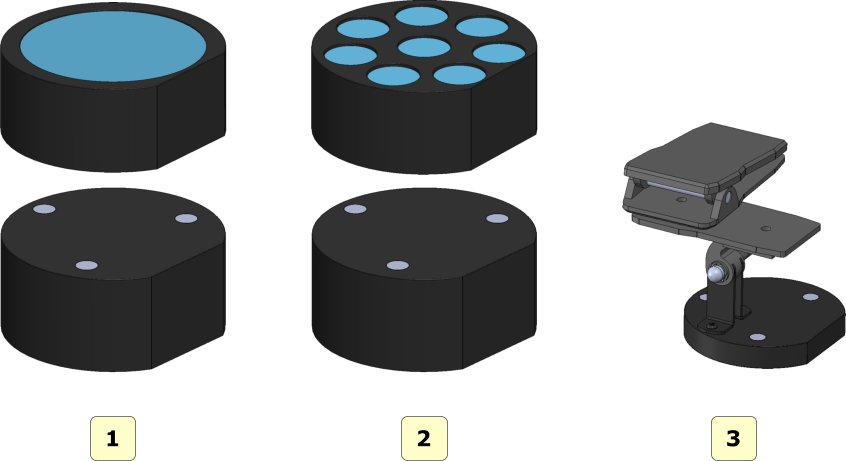
Scanning plates supplied
The image below shows all scanning plates supplied with the MDS500 scanner:
- 1 interface plate;
- 2 arch plate;
- 3 multi dies plate;
- 4 impression plate;
- 1 use this configuration to scan single dental arch or upper and lower arches in occlusion;
- 2 use this configuration to scan removable stumps;
- 3 use this configuration to scan impressions;
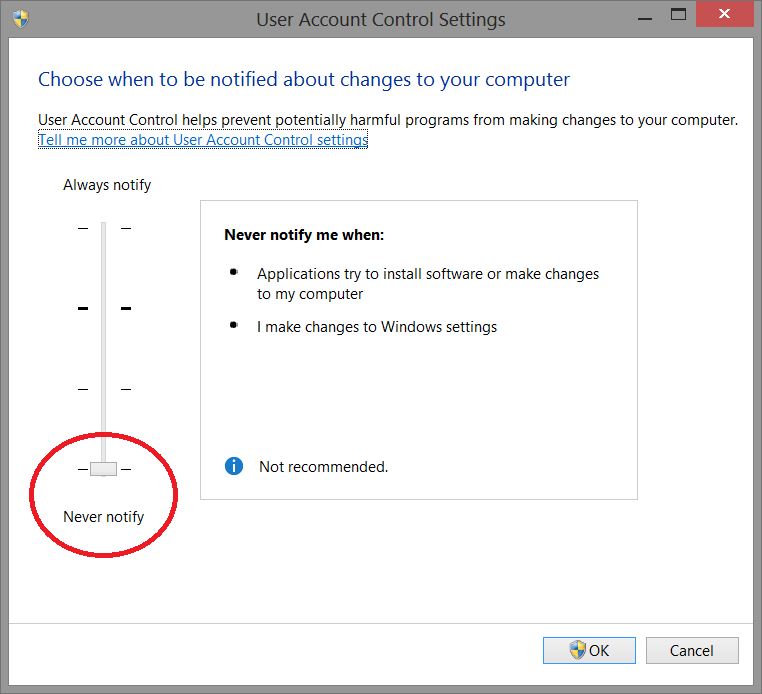
UAC - User Account Control
To avoid difficulties and limitations in the use of the Software, it is necessary to set the UAC slider - User Account Control to the minimum value as shown in the picture below.
To log in to the setting window: Control panel-> User Account-> Change Settings User Account Control.
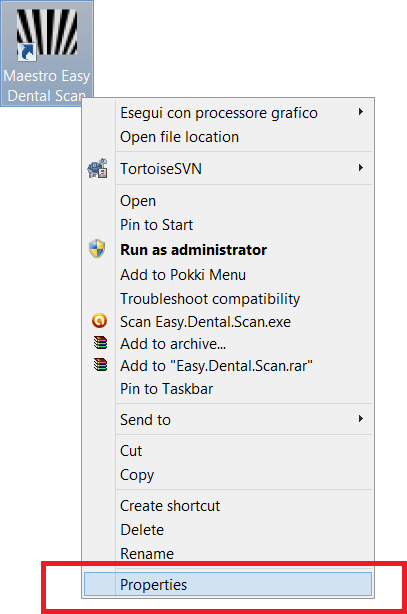
Administrator's Rights
In order yo put in operation the Software it is necessary to set correctly administrator's rights.
Follow the instructions as shown in the pictures below.
Right button of the mouse on the Software's icon to start the contextual menu and select the entry properties.
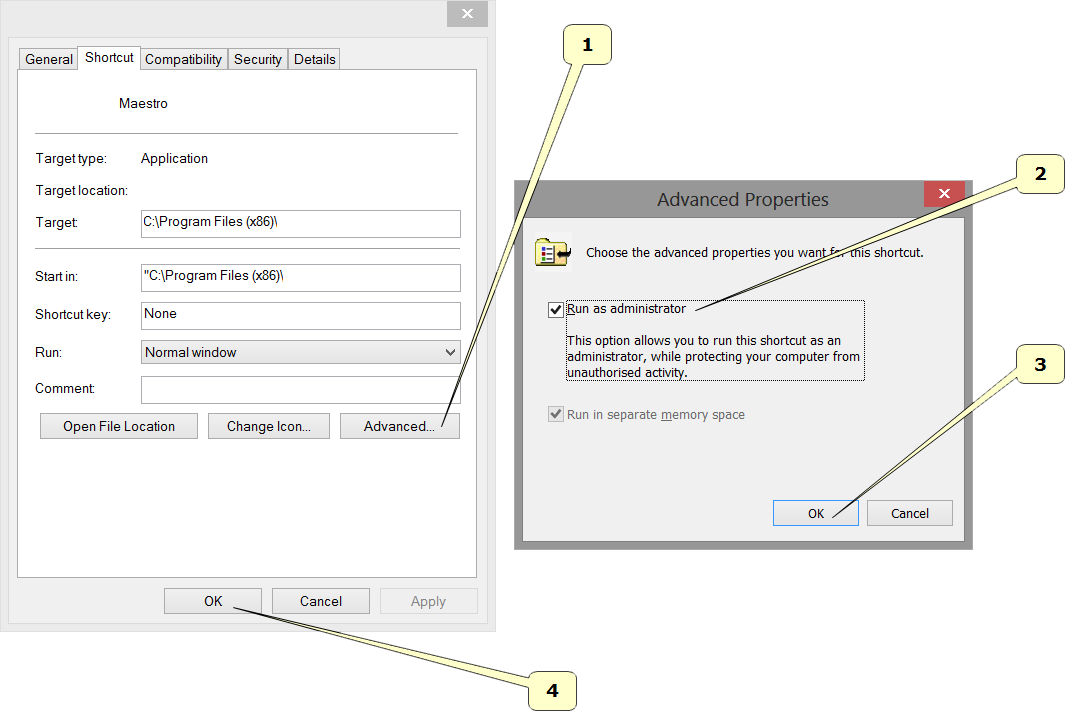
Follow the steps as shown in the sequency from 1 to 4.
- Press the button Advanced.
- Select the voice Run as administrator.
- Press the button Ok.
- Press the button Ok.
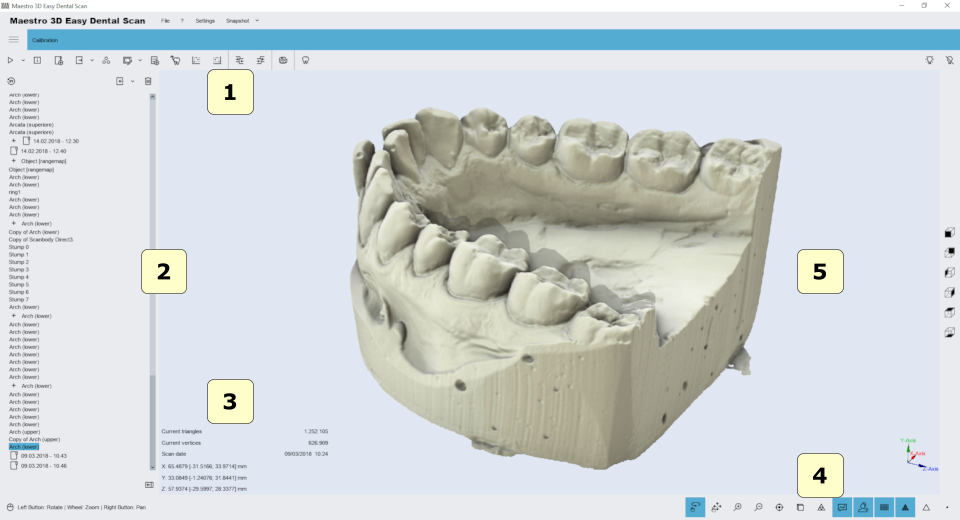
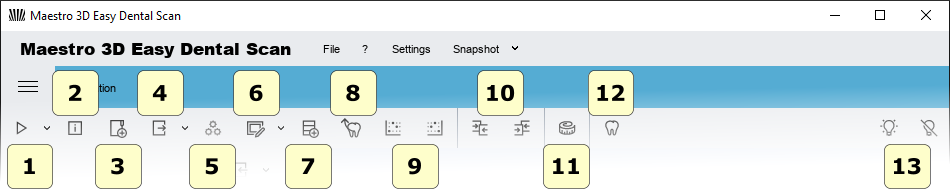
User Interface
The figure below shows the composition of the user interface.
- 1) Main Toolbar.
- 2) Tree Area.
- 3) Info Area.
- 4) Bottom Area.
- 5) Visualization\Editing Area
Main Toolbar
The main toolbar allows the access to all functionalities of Easy Dental Scan Software.
- 1) New Acquisition - Start a new scan or define a new scanning strategy.
- 2) Scanner Status - Activates the window that monitors the hardware scanner status.
- 3) New Group - Adds a new group in the tree. It's possible to move the elements of the tree inside/outside a group by mouse drag and drop.
- 4) Export - Export the selected item along the Z or Y Axis. You can export in open STL file or PLY file format.
- 5) Postprocess (convert scanned data into a 3D model) - The function is enabled when an item is selected not postprocessed. This operation can take a few minutes to converts the scanned data from the scanner in a triangular geometry.
- 6) Editing filter - Edit the selected items. This is useful for removing artifacts due to scanning, to remove the putty scanned, for make the holefilling, the decimation, 2D\3D selection edit, etc.
- 7) Import a scanbody from library.
- 8) #Stumps_registration automatic alignment procedure of the stumps.
- 9) #Manual_3-2-1_alignment set the selected item as fixed or floating in the manual align procedure.
- 10) #3D_Comparison.
- 11) Free Measures:
- point-point measures.
- angle measures.
- 12) CAD - send selected items to the design software.
- 13) Projector status.
- Power on.
- Power off.
The calibration tab is described here: Calibration.
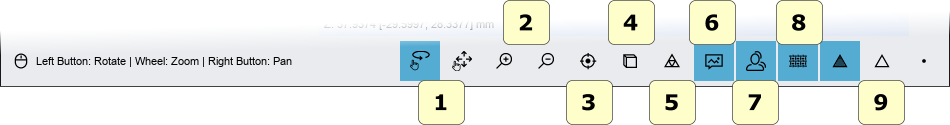
Bottom Toolbar
The bottom toolbar is the area of the screen containing a progress bar that is displayed and updated during each computation of the program and the controls for changing the visual settings of the visualization/editing area.
- 1) touchscreen mode (Rotate/Pan).
- 2) magnify in [Key PGDown]/magnify out [Key PGUp].
- 3) reset trackball [Key R].
- 4) parallel projection [Key O], perspective projection [Key P].
- 5) smooth shading [Key S], flat shading [Key F].
- 6) photorealistic rendering.
- 7) shadow, (available if photorealistic rendering is enabled).
- 8) texture color, (real object color).
- 9) show/hide triangles, edges [Key E], vertices [Key V].
Visualization / Editing Area and Info Area
The visualization / editing area is the area of the window in which the models are visualized and all the editing operations are performed.
In the visualization area it is possible to see the models and edit and measure distance between different point.
In order to examine the models displayed in the visualization / editing area camera parameters (position, scale and rotation) can be setted using an instrument called trackball.
The trackball is very simple to use. Just use the Left mouse button dragging to rotate around the model, the mouse wheel to Zoom in / Zoom out and the Right mouse dragging to move (pan) the camera.
The info area of the screen shows the info related to the current item.
Tree Area
The Tree Area contains all the models scanned. The Tree Area organization has a tree. The use of groups allows you to keep an ordering of the models scanned. To select a model from the Tree Area just click on it with the left mouse button. The models selected will be displayed on Visualization Area. To select more models click by holding down the CTRL\SHIFT key.
The Tree Area can contain the following elements:
| |
Stump |
| |
Upper Jaw |
| |
Lower Jaw |
| |
Upper\Lower Gingiva |
| |
Upper\Lower Waxup |
| |
Maxillary\Mandibular Relationship |
| |
Rangemap |
| |
Group |
For each of these elements there is associated a set of operations accessible via enabled icons in the Main Toolbar. These allow the user to access the main functions of the software.
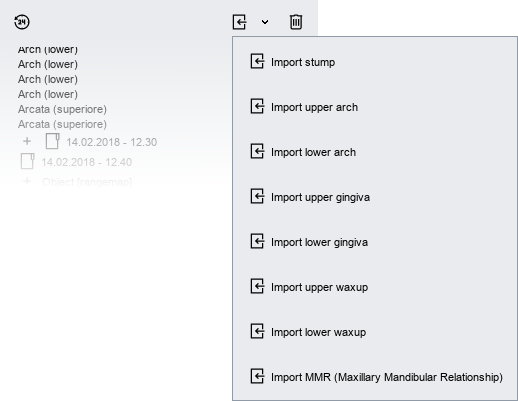
By accessing the drop-down menu as shown in the following figure, you can import into the tree the STL file.
Target objects
Some examples of target objects:
- Maxillary and Mandibular relationship
- Upper-Lower Jaw
- Other examples of dental arch
- Impression
- Stumps
Proper positioning of objects
Arch or MMR
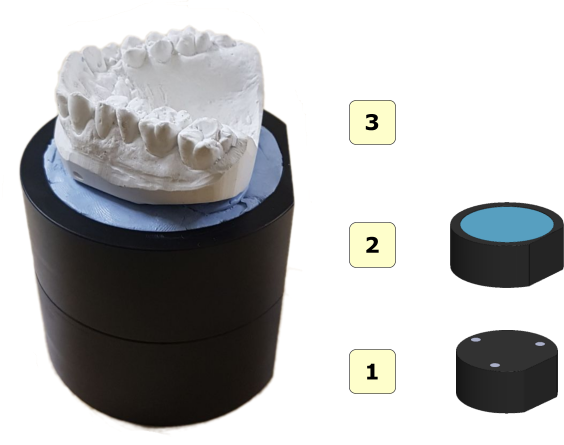
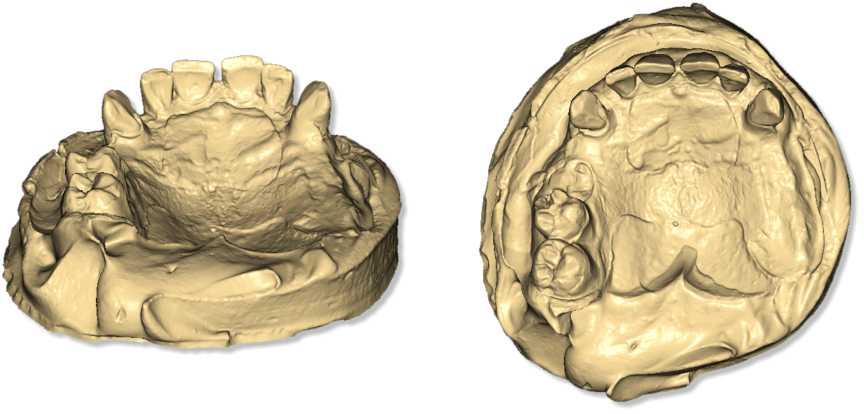
In the following images the correct positioning of the models on the rotary table is showed. The image below shows an arch correctly positioned on the rotary table. The arch should be placed at the center of rotary table supported by the putty or any other adhesive that keeps it well anchored to the table.
The arch should be parallel to the surface and should not be tilted.
- 1 interface plate;
- 2 arch plate;
- 3 object to scan, arch or maxillary mandibular relationship (MMR);
Multi dies
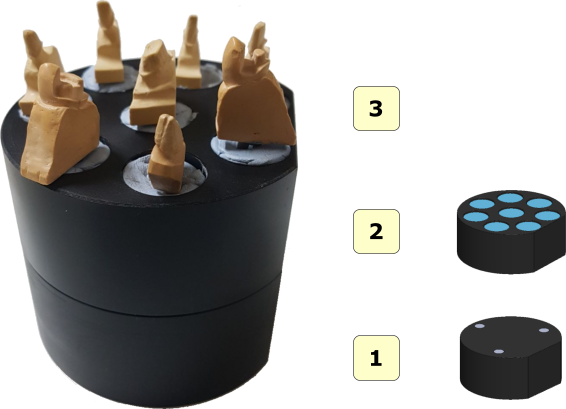
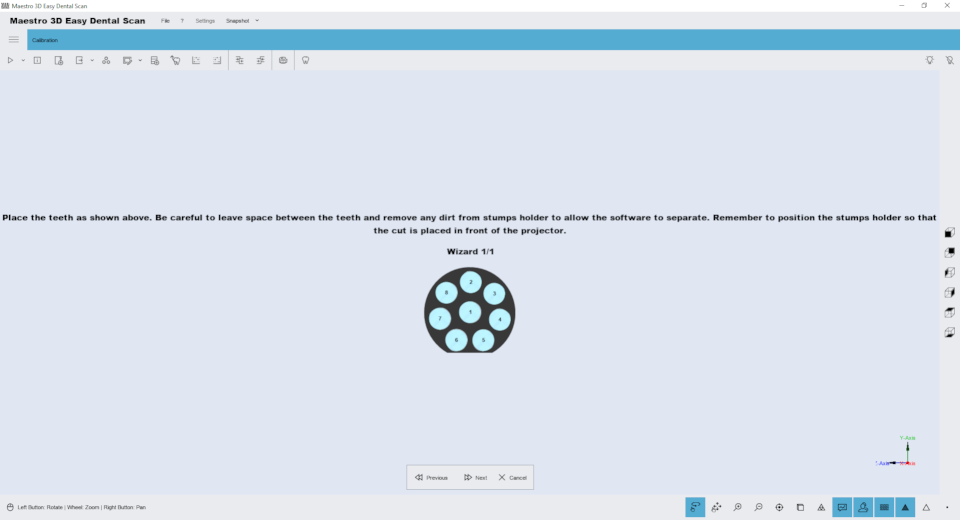
It is possible to put on the rotary table of the scanner more stumps simultaneously. See the following pictures to observe the proper placement of stumps. After the scanning process, the software automatically recognizes and separates the individual stumps, adding an item in the Tree Area for each acquired stump. The pictures below show how to correctly place the stumps on the rotary table of the scanner. The scanner may be equipped with a multidie plate of 8 teeth.
- 1 interface plate;
- 2 multi dies plate;
- 3 stumps;
The numbering (1..8) on the plate meets the numbering of the elements added to the Tree Area only if the plate is placed in front of the scanner. When working with more than a stump it is absolutely necessary that adhesive putties sustaining stumps and the body of each stumps will be separated at least some millimeters from each other. In this way the scanning software is able to recognize each stump, see the correct stumps position in the picture below:
An example of incorrect positioning:
|
WARNING Shown in the picture above an incorrect positioning of the stumps. The support of the putty of each stumps should not join and the bodies of the stumps shall not touch or should not be too close because this incorrect positioning prevents the scanning software to identify and separate the individual elements. |
|
TIP The stump/s should not be placed with an excessive inclination, because the scanner is not able, in these conditions, to acquire all the margin line. So you should always place the stumps perpendicular to the rotary table surface. |
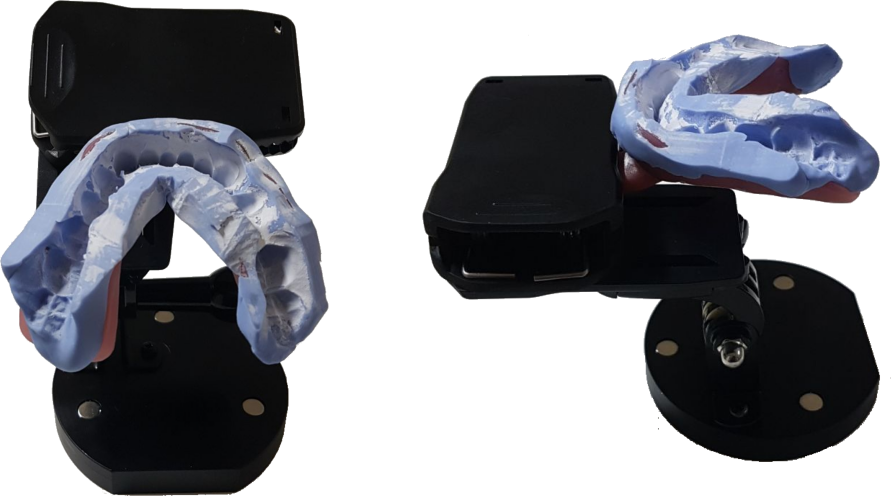
Impression
The following images show the correct positioning of the impressions on the rotating table. This fixing system, used in conjunction with the Smart Impression Scanning feature, is only available for MDS 500 models. The image below shows an impression correctly positioned on the rotating table. The impression must be attached to the special clamp so that it is in the center of the rotating table. You can also use the wheel to adjust the angle.
It is not necessary to use other plates, the impression fixing system must be positioned directly inside the scanner.
|
TIPS
|
3D Scanning
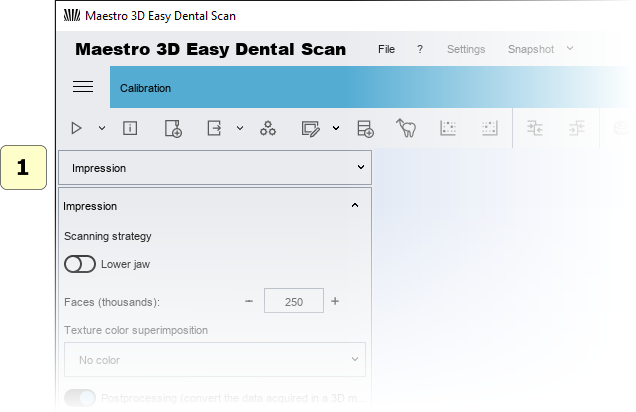
Scan parameters
To start a new acquisition just press New acquisition in the Main Toolbar.
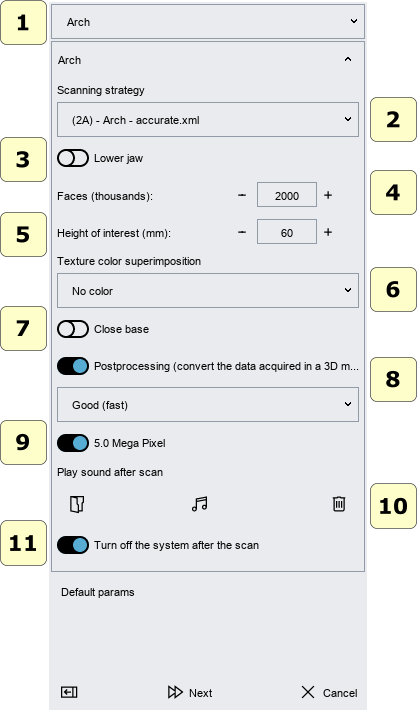
Through this window you can choose the type of object to be scanned and the scanning parameters.
- 1 object type (arch, gum, waxup, stumps, impression, maxillary-mandibular relationship, ...).
- 2 scanning Strategy: it's possible to choose a scanning strategy.
|
WARNING It may happen that with a low number of acquisitions (eg 4-5) for certain models may fail to scan because there is not sufficient overlap geometry between the various shots. In this case it is sufficient to increase the number of acquisitions into the strategy. |
- 3 upper or lower model.
- 4 faces (triangles):
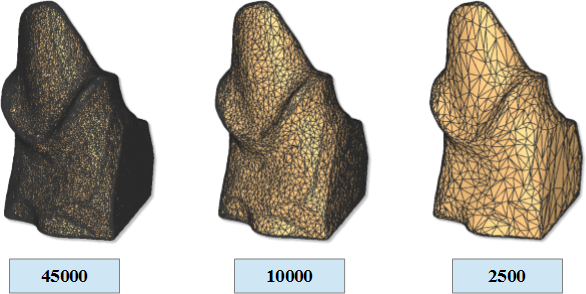
This number defines the number of triangles you want in your final model. The figure below shows the same model with 45000, 10000 and 2500 triangles. The precision and accuracy in the 3 models is equivalent. Among the 3 models changes the number of triangles that approximate the surface geometry. The system acquires always at max precision and max accurancy. Only after obtaining the final three-dimensional model at max number of triangles, it is decimated to obtain the desired number of triangles. Is also possible to decimate the model later.
|
WARNING Greater is the number of triangles, greater is the size of the STL file.
|
Recommended values:
| Arch\Gum\Waxup\Impression | 180000 - 250000 triangles |
| Stump | 15000 - 45000 triangles |
| MMR | 180000 - 200000 triangles |
- 5 height of interest:
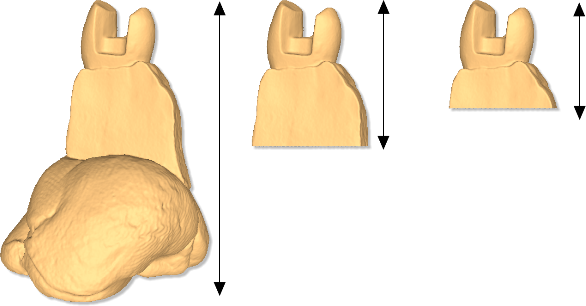
This param allows you to choose the height of interest of the model, (this height value is measured starting from top to bottom).
First picture (from left to right) shows the model of a stump where the height of interest parameter is disabled and then the stump is acquired entirely including the adhesive putty support that sustains it. Subsequent images display the same stump with the height of interest parameter set at 20 mm and 15 mm respectively (as can be seen the adhesive putty support is automatically removed).
It is important to remember that, in order to make the best use of this parameter, the model (arc, one or more stumps, etc...) must be placed perpendicular to the surface of the rotary table.
|
IMPORTANT Cut the model choosing the height of interest reduces the computation time of postprocessing and can improve the quality of the results. (Especially a smaller volume of the point cloud of the stumps can lead to a better yield of the final model). |
In any case, you can always remove the not interesting geometry, at any time, by editing the model.
- 6 texture Color Superimposition:
This requires the Texture Color Superimposition module active. The activation is carried out through a software license. This is useful to obtain models with a RGB color texture or grey scale color texture. For example it helps create very accurate margin lines as marked on the model.
- 7 close base:
If this option is checked, the software close the bottom base of the model automatically.
- 8 postprocessing (convert the data acquired in a 3D model):
If this option is checked, the system automatically postprocessing the data acquired and it builds the triangular geometry surface. If it is not checked the data will be not postprocessed. It is possible postprocess the data acquired later.
- Good (fast): this option is recommended.
- Best (slow): this option take more computation time and make a 3D models with more details.
|
TIPS To reduce the time of interaction with the scanner, where you have many models to be scanned is advisable not to make the postprocessing after each scan. In this case it is recommended scan all model (not check the option "Postprocessing", no check the option "Turn off") and at the end of the work, turn off the system and select from the tree area all items (rangemaps) and press button to postprocess all models. |
- 9 cameras resolution, (available only with MDS 500 model scanner).
- 10 play sound after scan:
It's possible to choose a *.wav file to play after the scan and after the postprocessing.
- 11 turn off the system after the scan:
Turn off the system after the end of the scan.
|
TIPS Remember to turn the system off when not in use to avoid wasting the lamp. |
Scanning process
This window shows the progress of the scanning phase. This may take a few seconds or a few minutes depending on the strategy chosen.
In the window on the left shows the 2D image acquisition and 3D image on the right.
After this operation, if the the option "Postprocessing" was checked the software automatically generates the surface of the model from the acquired points, and adds to the Tree Area a new element. Then selecting it in the Tree Area, the model is displayed into the Visualization Area.
If the option "Postprocessing" was not checked, the software adds to the Tree Area a new element with a greyscale icon. Before you can perform any operation of this model is necessary to postprocess the data acquired.
|
WARNING Before scanning make sure that the model is correctly positioned on the rotary table and that the front door of the scanner is closed. During the scan please don't move neither the scanner nor its support plane. |
Scanning Strategy
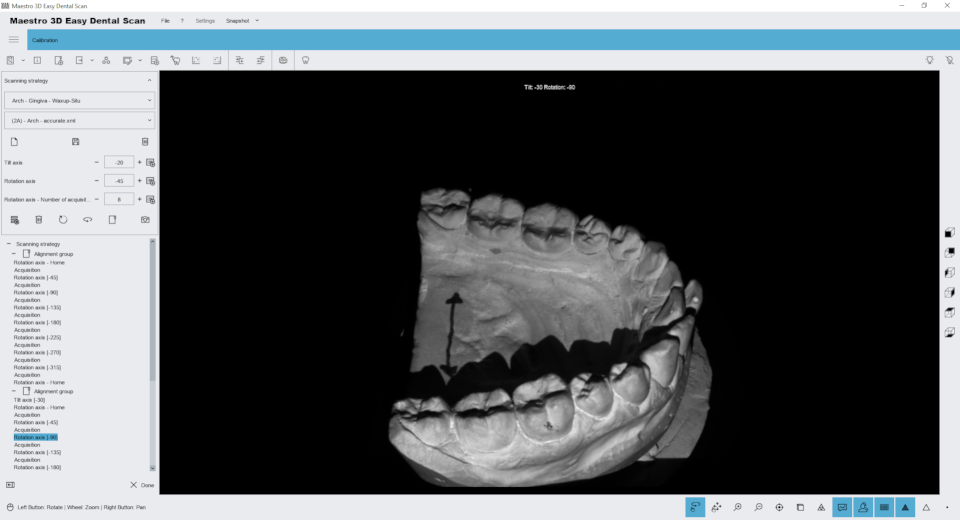
The following image shows the window for managing the scanning strategies.
See below for details:
- 1) Scanning group: MMR, Arch, Stumps, Impression.
- 2) Strategy name.
- 3)
- New Strategy.
- Save current Strategy.
- Delete current Strategy.
- 4) Add tilt command (before adding the command selects the rotation degrees).
- 5) Add rotation command (before adding the command selects the rotation degrees).
- 6) add a batch acquisition. (before adding the command select the number of rotary table steps of the rotary Axis).
- 7) Commands:
- Clear all commands.
- Delete selected command.
- Add tilt home position command.
- Add rotation home position command.
- Add an alignment group.
- Add a single acquisition.
- Start the strategy simulation.
|
TIPS:
|
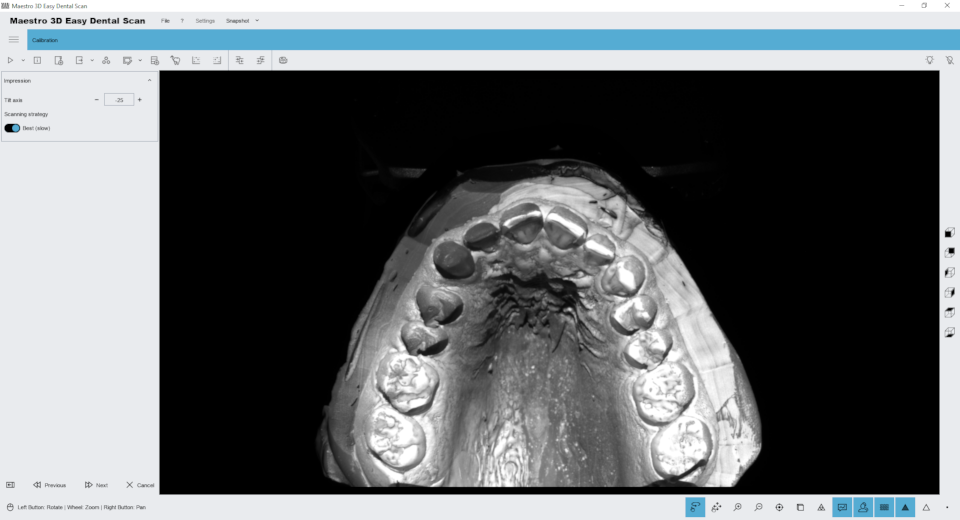
Impression Scanning
The following image shows in detail the parameters to be selected to scan the impression:
- 1 select impression from the drop-down menu and choose the rest of the parameters as you prefer.
Preliminary to this, see the correct positioning of the impression on the appropriate impression plate: #Impression
The image below shows the next step.
In this phase the tilt motor must be adjusted so as to be able to visualize the impression as shown in the image above. The goal is to give the software an excellent point of view, for example, that the incisors are clearly visible, both vestibularly and lingually. From this starting point the software will build a dynamic scanning strategy that allows the best possible acquisition of the impression. Try to adjust the inclination value so that the incisors are visible as much as possible. Let's see in detail the interface tools:
- 1 press the button + or - to move the tilting axis;
- 2 select this if you want to use the best strategy. This takes more time but guarantees greater coverage;
|
CONSIGLO:
|
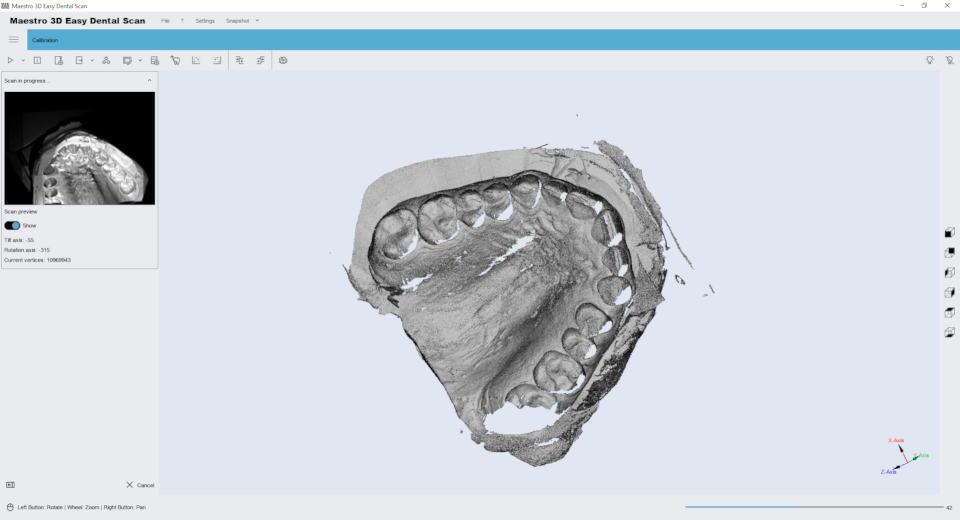
The next step as shown in the image below is the scanning phase. During this phase it is important that the scanner door is closed so that the ambient light does not interfere, reducing the contrast of the structured light. It is equally important that the scanner be placed on a stable table and that it will not be shocked or vibrated during this phase.
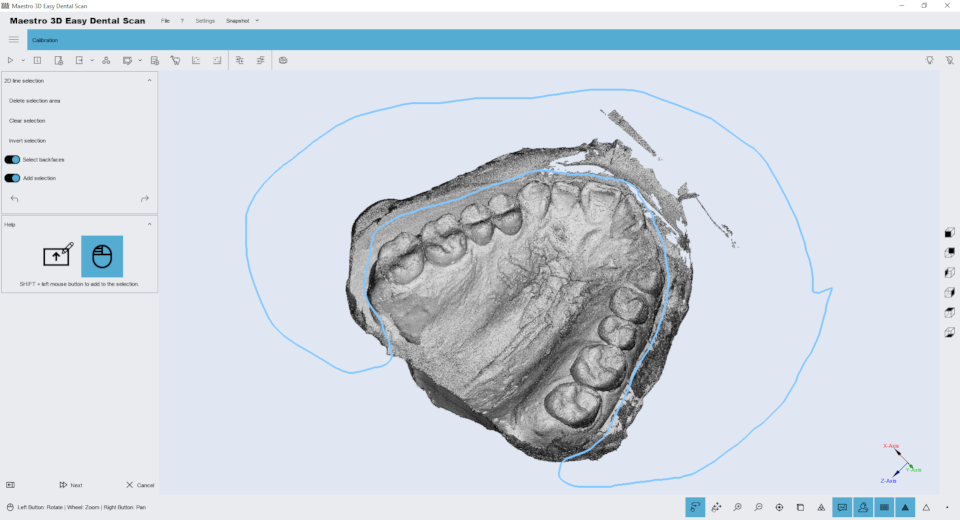
Once the impression scan is complete, the software allows you to "clean up" the scan before processing it. See also the function of #Editing_with_2D_selection. In this phase, as shown in the image below, it is possible to remove all the excess parts of the scan.
In this way, the post-processing phase that converts the point cloud into a 3D model will be faster and more effective.
Below you can see the finished result of the impression scan:
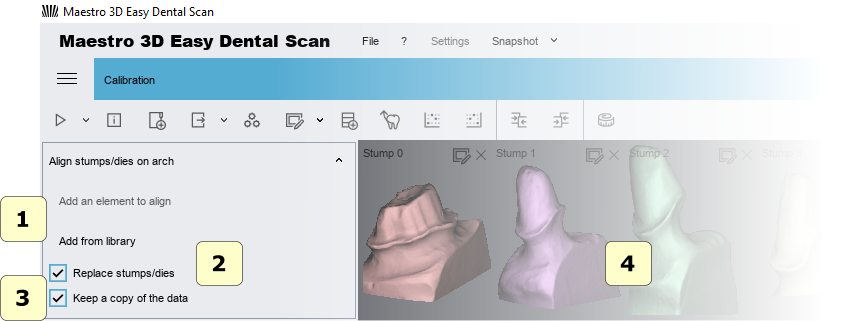
Stumps registration
The registration of stumps is totally automatic and it allows to replace the low resolution stumps, acquired with the arch, by the high resolution stumps acquired without the arch.
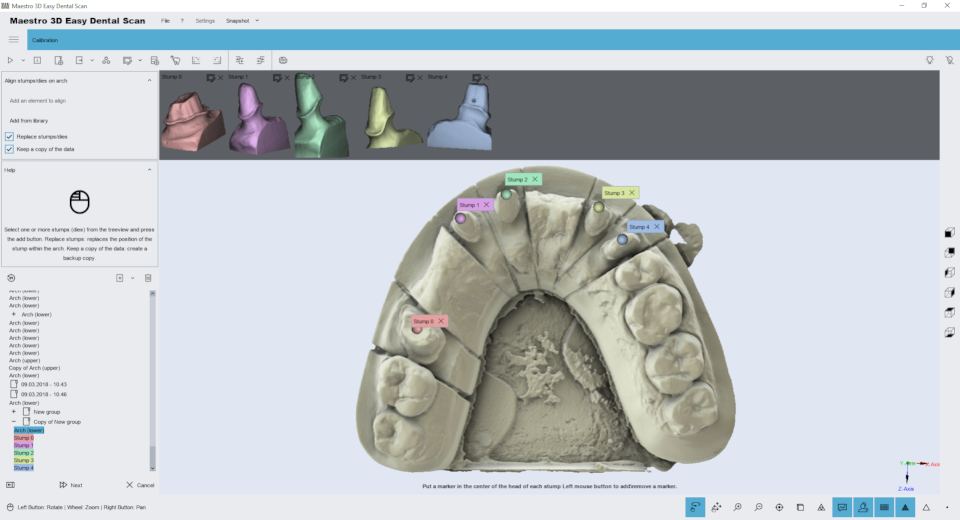
Select into the Tree Area the arch with the stumps (which are to be replaced).
After the arch is displayed in the Visualization Area with a constrained view so that it can be inspected only from above. In details:
- 1) to add the stumps\scan body to substitute, select these from tree area and press the buttons.
- 2) if replace stumps is checked, the high resolutions of the single stump will be replaced with the lower resolutions stump scanned with the arch. This is recommended if you need to work with a dental cad software. If not select this option the stump will be only aligned.
- 3 if this option is checked the software make a backup copy of the data.
- 4) preview area of the stumps.
|
TIP: If the selected stump is not the correct stump, just close the preview window to remove it from the registration process. You can register up to 16 stumps simultaneously. |
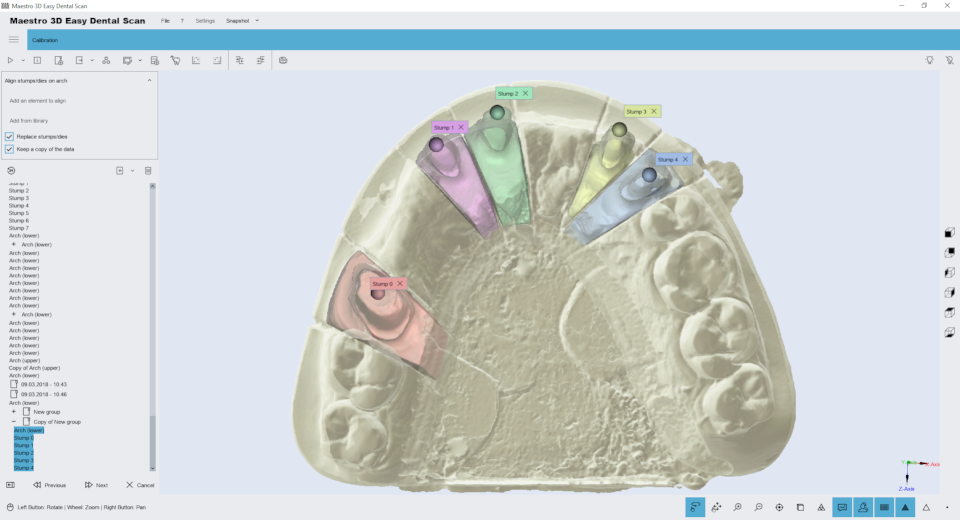
After having selected and added the stumps, press double click with the left mouse button over the center of the head of the low resolution stumps to indicate the position where every stump must be registered.
By double clicking over the head of the stumps, it is added to the Visualization Area a sphere (called marker) associated with a number. Color and number, as shown in the picture, these are associated with the right stump.
|
TIP: To remove a marker double-click on it. |
Before to proceed with the registration, please make sure that each marker is associated with the right stump. To proceed with the registration press the Next button.
A progress bar placed in the Bottom Toolbar will indicate the progress of the registration process.
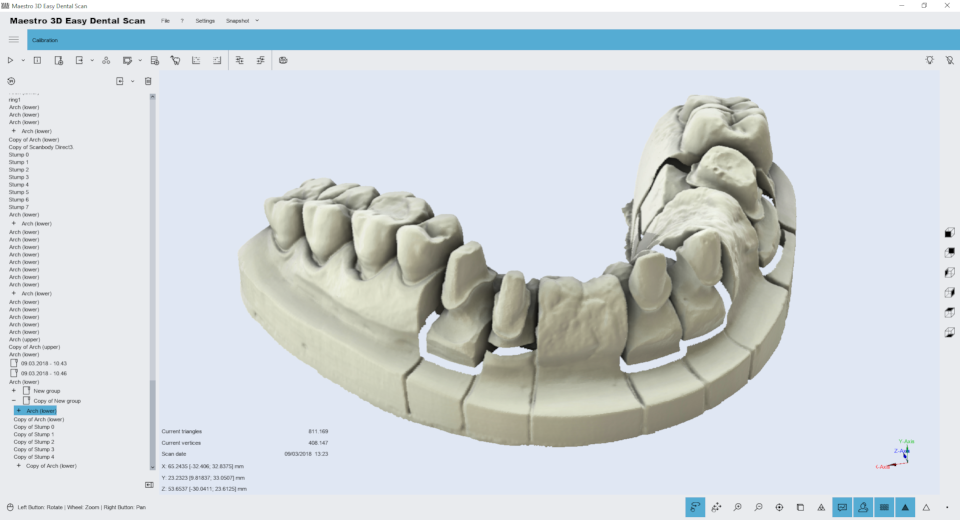
At the end of the registration process the result of the registration is displayed in the Visualization Area, where low resolution stumps have been replaced with high resolution stumps.
If you are satisfied with the result press the button Next to finish and save the registration obtained or press the previous button to return to previous step.
If one or more stumps are not correct aligned, press the close button near the marker and then after having completed this task you can re-register only those stumps.
If the registration is not satisfactory, please verify that markers have been placed in the correct position as explained previously (in the center of the head of each stump and in the correct order).
|
TIP: It is also possible substitute the stumps on the arch with a manual alignment. |
Manual 3-2-1 alignment
With the manual registration process, is possible to align any pair of models. For example useful to align a stump on an arch or an arch or bite with a antagonists reference model.
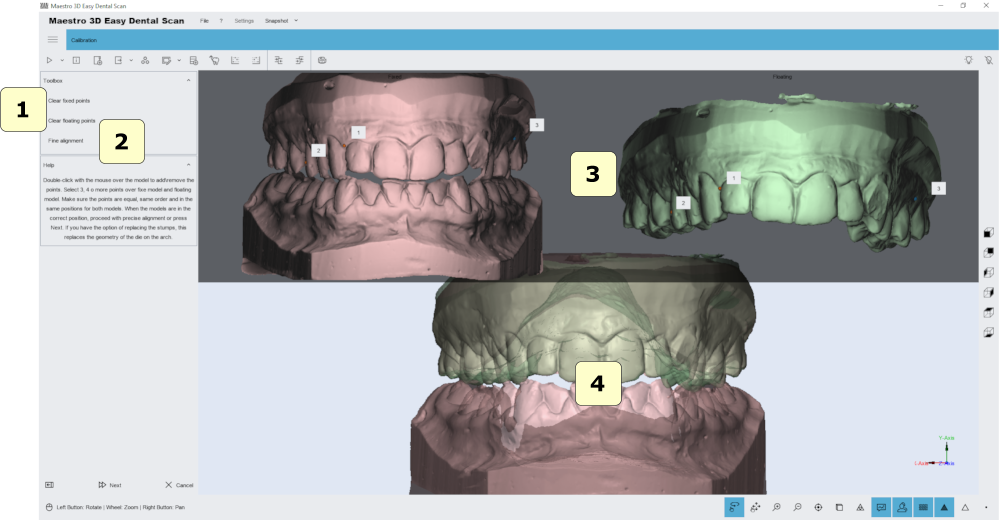
To align two models, need to select the fixed model (example maxillary mandibular relationship) and the floating model (example arch). The next image shows the manual alignment window.
To align the floating object over the fixed object, you have to add some points in the fixed model (that appears to the left of the screen) and the same points should be added to the floating object (that appears to the right of the window). You must add at least 3 points on each model.
- 1) clear fixed or floating point.
- 2) fine alignment. Improves the initial alignment given by the points entered by the user.
- 4) preview area where are showed the fixed and floating model.
- 5) alignment result.
|
TIP: Press double click with left mouse button to add a point over the model. |
Editing Filters
Editing with 2D rectangle
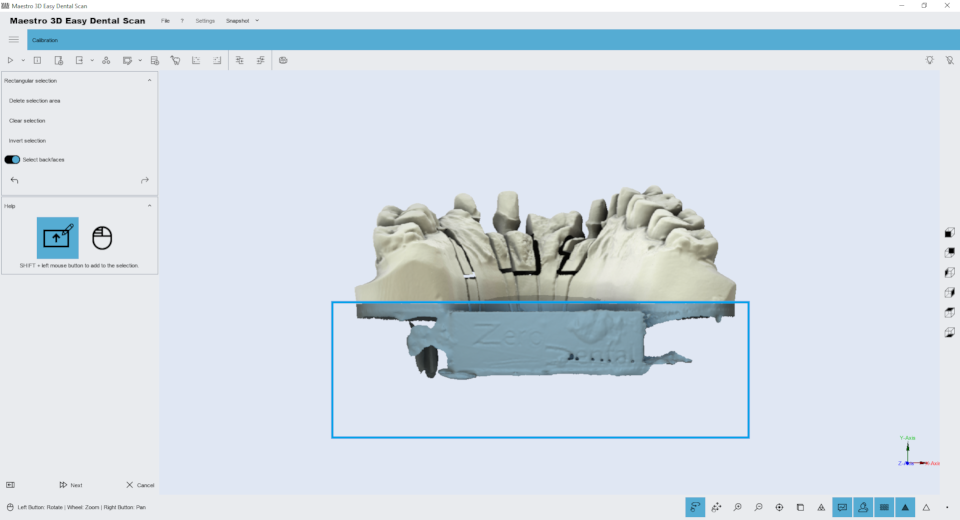
Editing features of the rectangular selection. The image below shows the filter window.
Holding down the SHIFT key and the left mouse button you can draw a rectangular selection area. The area of the selected geometry will appear colored red. In the toolbox on the left side of the screen there are buttons to delete the selected area, invert the selection, clear the selection. To save the changes and return to the previous screen, press the button Next.
Editing with 3D polyline
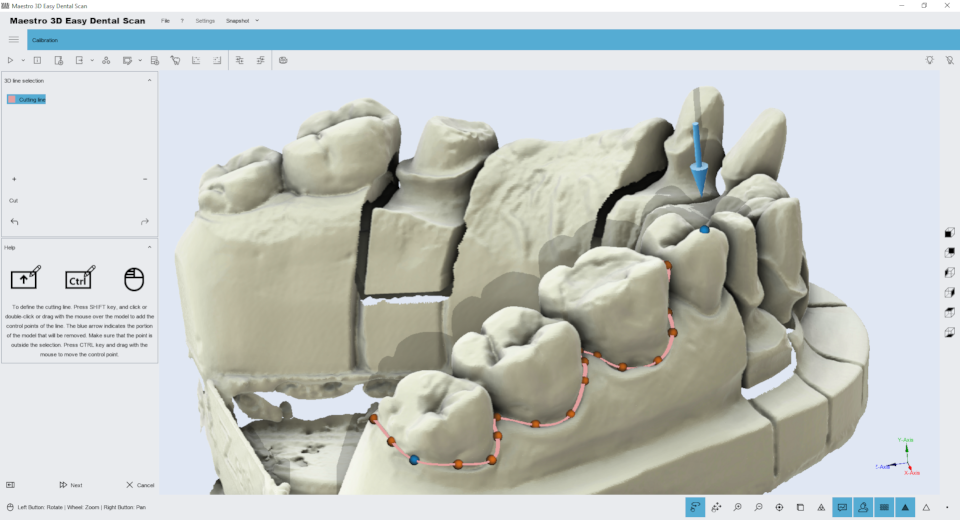
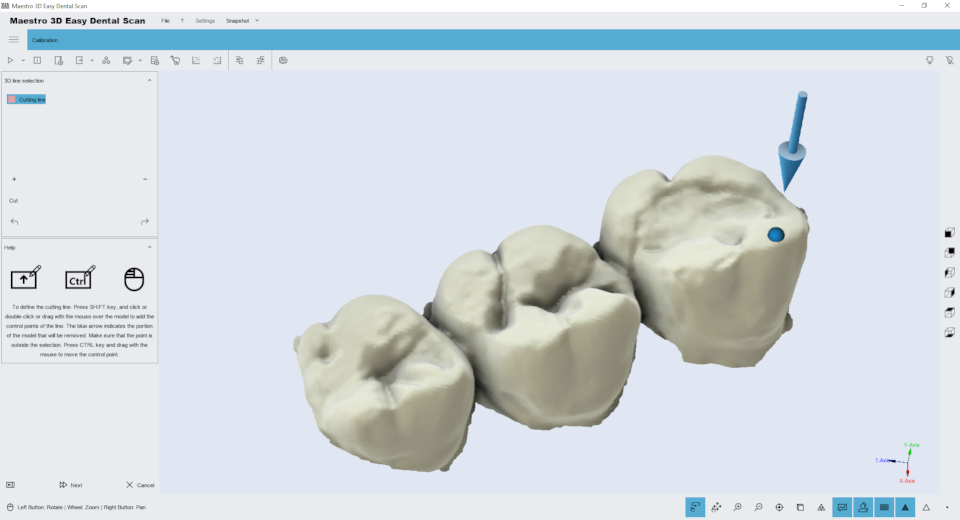
Editing features of the 3D polyline selection. The image below shows the filter window.
Holding down the SHIFT key and the left mouse button you can draw a 3D polyline over the model. This function is useful to remove the gum or the waxup from a model. After you have drawn the polyline just double click into the area that you want to delete. The image below shows the result of the filter.
To save the changes and return to the previous screen, press the button Next.
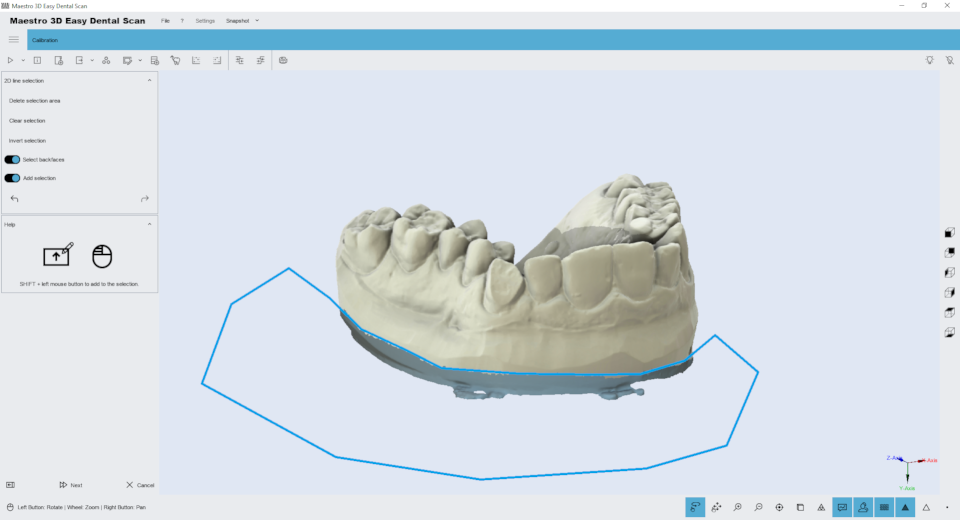
Editing with 2D selection
Editing features of the 2D selection. The image below shows the filter window.
Holding down the SHIFT key and the left mouse button you can draw a 2D selection area. The area of the selected geometry will appear colored blu. In the top of the screen there are buttons to delete the selected area, invert the selection, clear the selection. To save the changes and return to the previous screen, press the button Next.
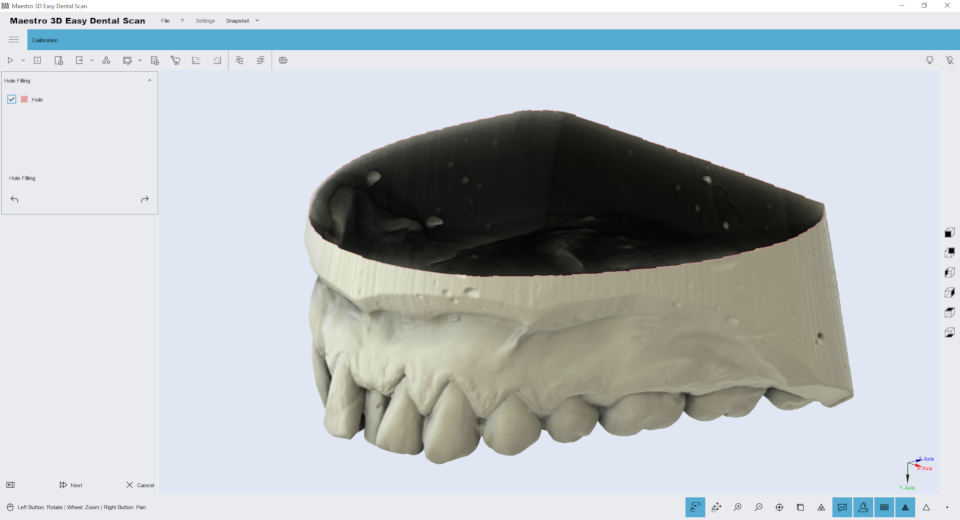
Holefilling
Editing feature of holefilling. The image below shows the filter window.
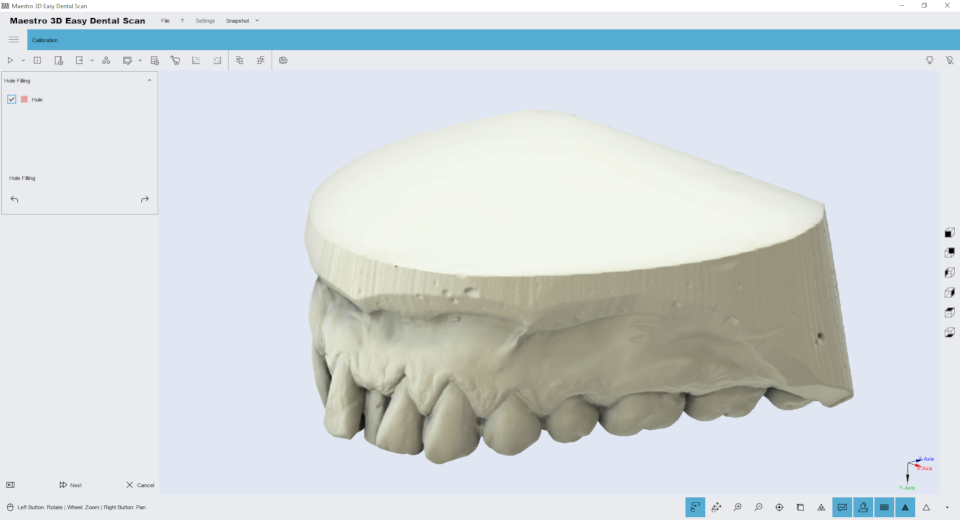
Just press the button Hole filling in the toolbox on the left side of the screen to filling all holes in the model. This is useful to fill the bottom of the base of a model. The image below shows the result of the filter.
To save the changes and return to the previous screen, press the button Next.
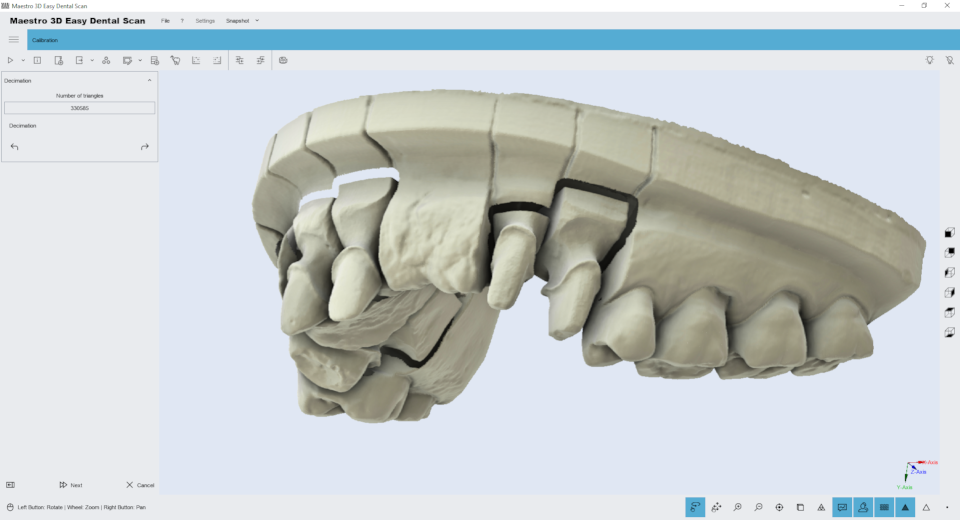
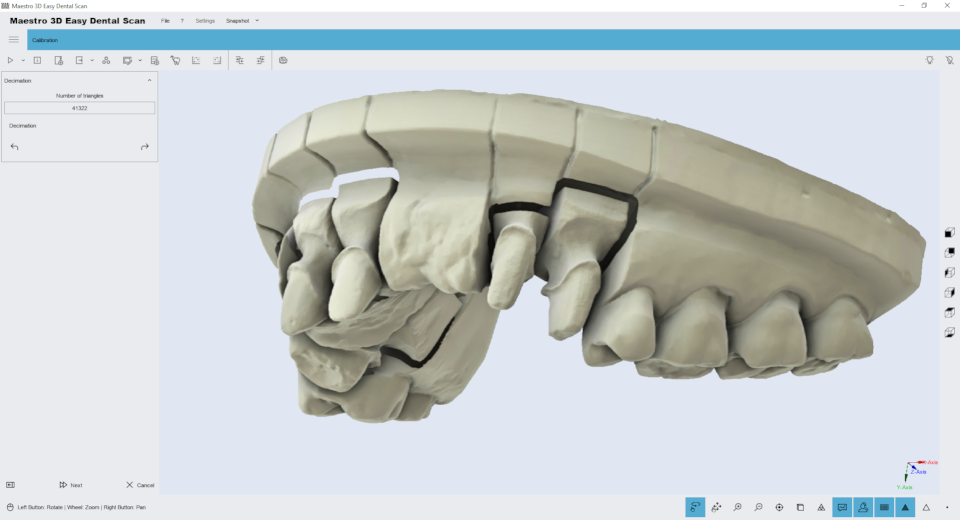
Decimation
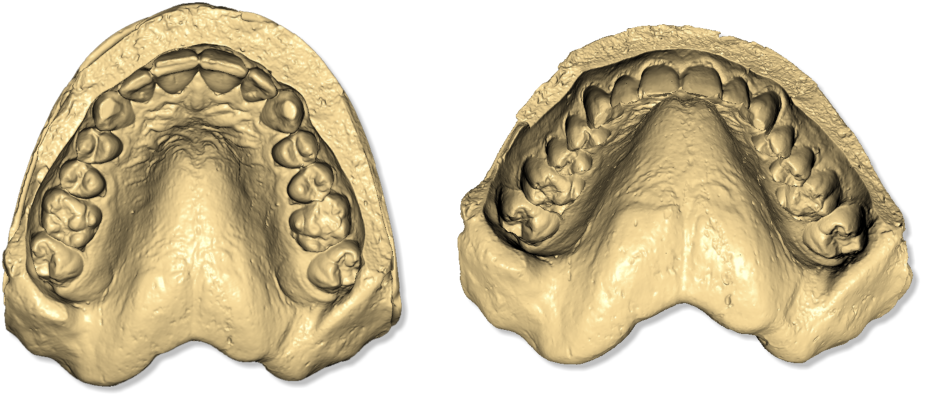
Editing feature of decimation. With this feature it is possible to reduce the number of triangles of the model. The filter removes more triangles in the model areas with less features, keeping better details in the most important areas of the model as the margin line or the teeth geometry. The image below shows the initial model at 700,000 triangles:
Just choose the triangles number and press the button Decimation in the toolbox on the left side of the screen to reduce the number of triangle of the model. To save the changes and return to the previous screen, press the button Next.
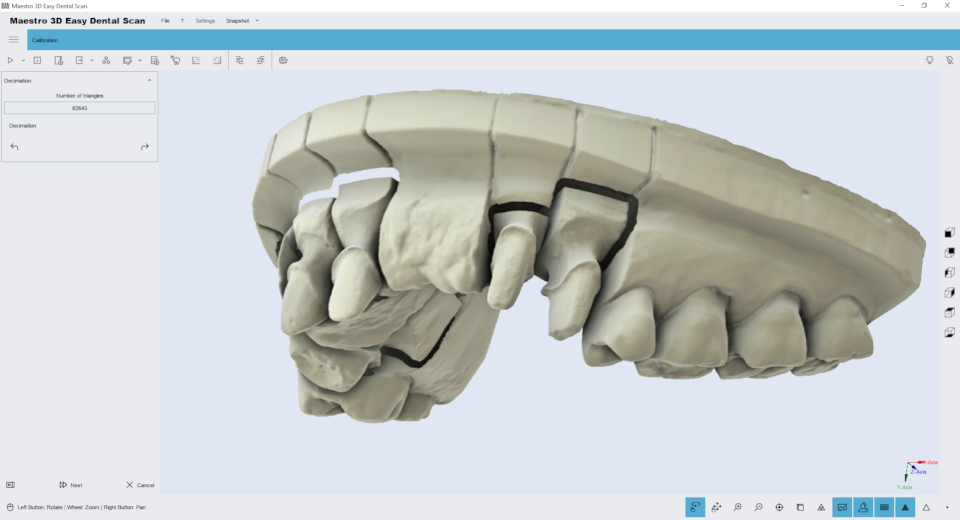
The image below shows the same model with a quarter of resolution, 160,000 triangles. As you can see, there is no loss of detail and the margin lines are still very visible and detailed.
we can see that even at low resolutions as shown in the image below, of about 80,000 triangles the quality of the 3D model is still appreciable.
3D Comparison
To perform the model comparison it is possible to select the "reference" model and the "test" model. The following image shows the 3D comparison performed on two different scans of the same model. As can be appreciated from the color map, the two models are practically identical.
|
TIP: before comparing two models it is necessary that they are aligned one on the other, through for example the function of #Manual_3-2-1_alignment. |
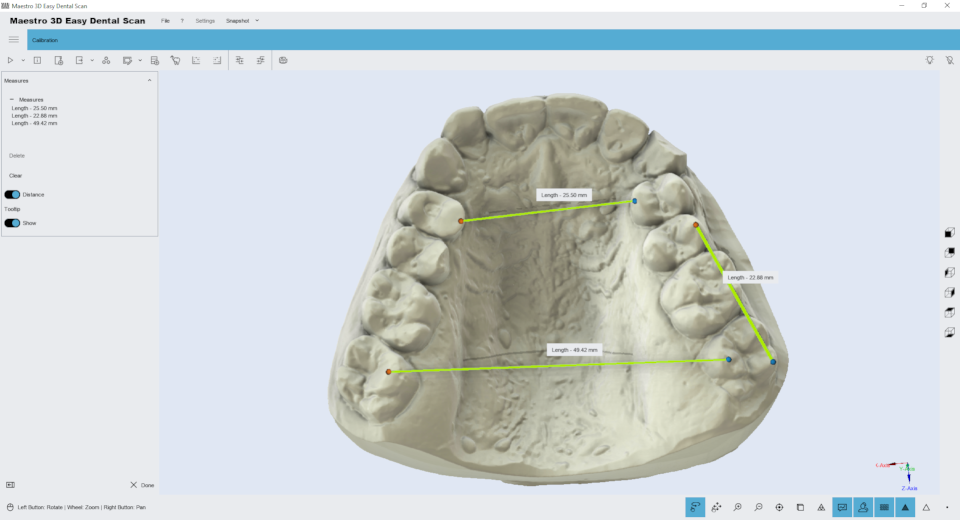
Free Measures
In order to perform the measures of length or angles, select the item to inspect and then goto in measures feature.
|
TIPS: double-click with left mouse button to add a point. |
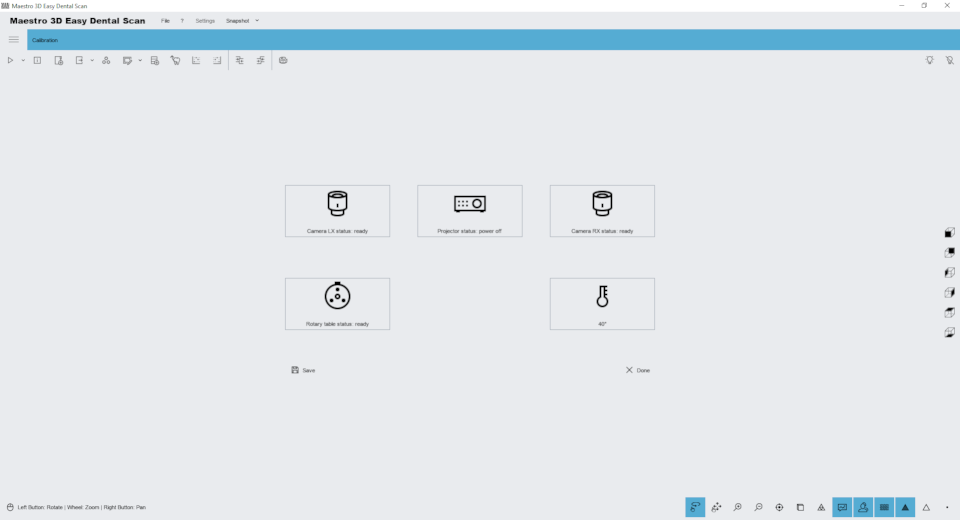
Scanner Status
Through this function, you can monitor the status of the scanner hardware. The window will show the status of each hardware device inside the scanner.
Dental Studio - Ortho Studio module Wizard
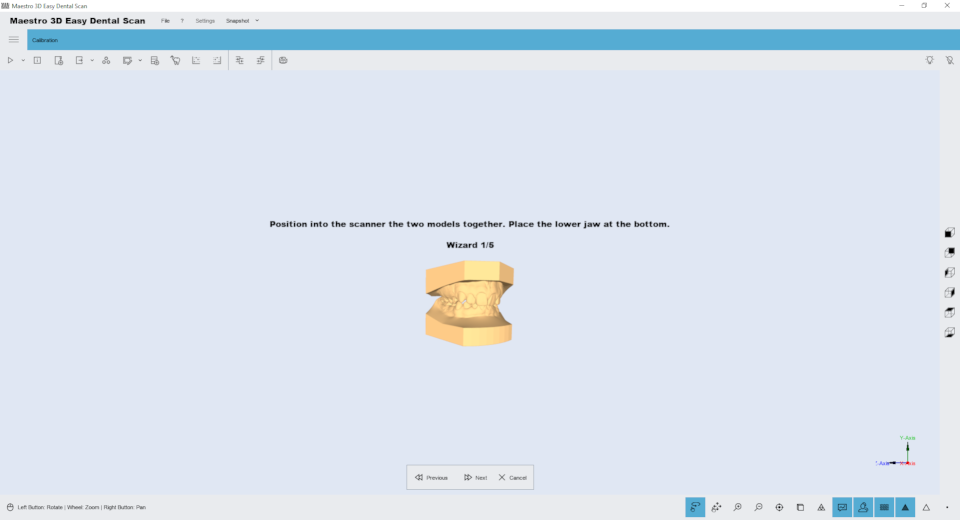
This scanning wizard helps the user to make all necessary scans and alignments to obtain a complete case to work into Dental Studio software - Ortho Studio module.
The following image shows the first step of the scan. In this phase you can scan maxillary and mandibular relationship. In this window you can change the scanning settings and the scanning strategy.
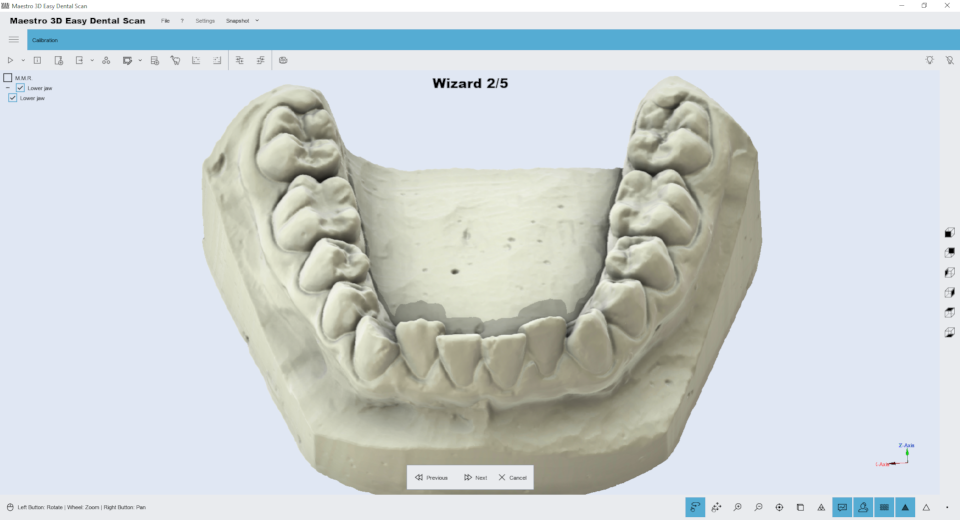
The following image shows the result of the maxillary and mandibular relationship. Now the user can scan the lower arch.
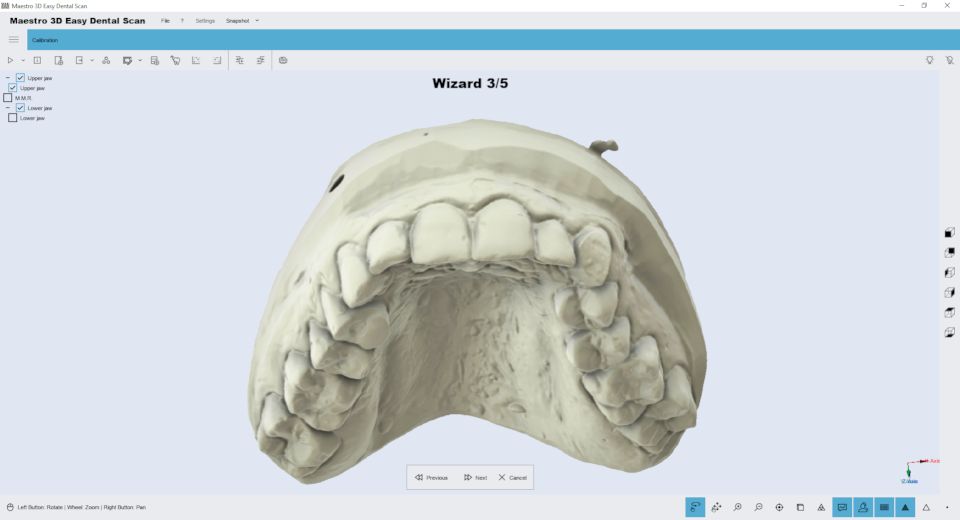
The following image shows the result of the lower arch. Now the user can scan the upper arch.
The following image shows the result of the upper arch. Now it's possible to perform the alignment of the upper and lower arch respect to the relationship. The procedure of alignment is the Manual 3 2 1 Alignment.
After that the scanning software send the correct data to the Ortho Studio software.
Dental Restoration Wizard
This scanning wizard helps the user to make all necessary scans and alignments to obtain a complete case to work into all dental cad integrated with Maestro 3D Scanner. All Maestro 3D scanners are fully integrated with leading design software such as exocad and Maestro_3D_Dental_Studio_-_User_Manual#Dental_restoration_.2F_Dental_CAD. The following image shows an example of a wizard step of the scan. In this window you can change the scanning settings and the scanning strategy.
Exocad Wizard
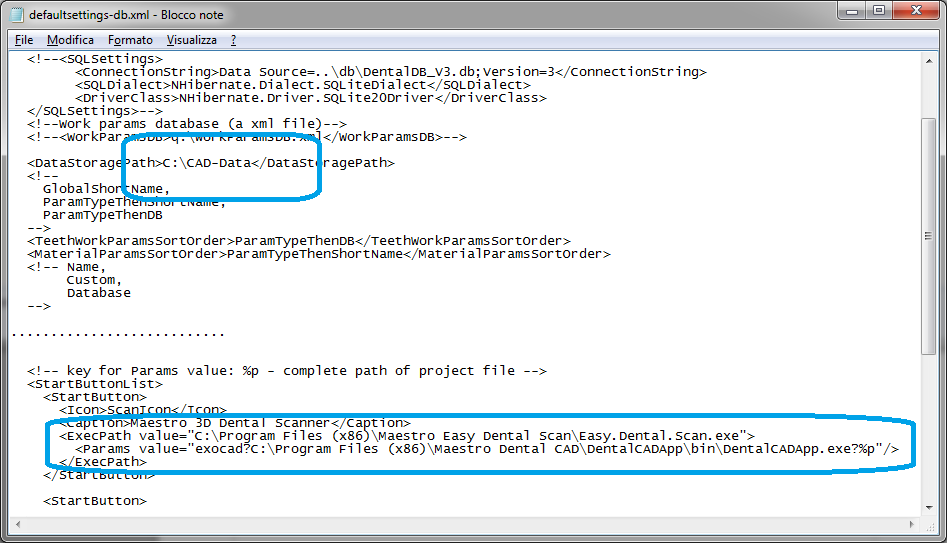
To integrate the scanner with the exocad software you need to edit the file \exocad-folder-installation\DentalDB\config\defaultsettings-db.xml as shown in the figure below.
<DataStoragePath>C:\CAD-Data</DataStoragePath>
...
<StartButtons>
<Button>
<Icon>ScanIcon</Icon>
< caption > Maestro 3D Dental Scanner < /caption >
<ExecPath value="C:\Program Files\Maestro Easy Dental Scan\Easy.Dental.Scan.exe">
<Params value="exocad?C:\Program Files\exoCAD\DentalCADApp\bin\DentalCADApp.exe?%p"/>
</ExecPath>
</Button>
...
- <ExecPath value = is the path where you have installed the Easy Dental Scan.
- <Params value = is the string exocad? and the path where you have installed dentalCADApp with ?%p at the end of the string.
Calibration
Calibrate a scanner model that is earlier than MDS500
Calibrate the MDS500
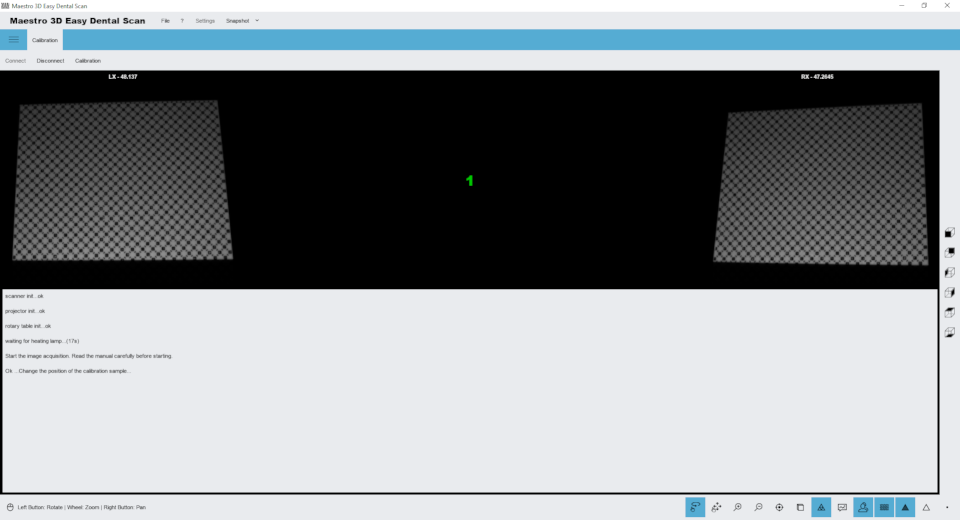
Click on the tab Calibration, place the calibration sample in the scanner and press the button Connect and once the images of the two cameras appear as shown above, press the button Calibration.
The calibration process is totally automatic, during this operation the optics, the motors and the relative axes are calibrated. Wait until a successful or error message appears on the screen. After this you can remove the calibration sample, store it and continue with the scans.
The calibration process takes a few minutes. It is advisable to keep the door closed during the calibration process and not to hit the table where the scanner is housed.
What is calibration?
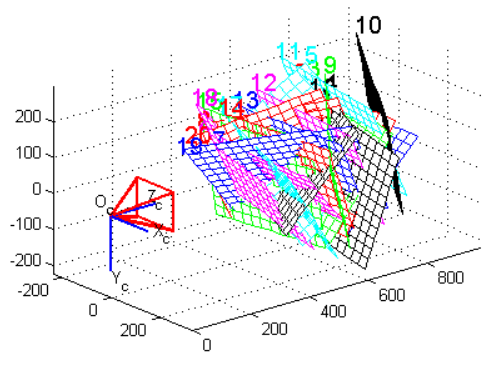
In a 3D scan system, calibrate a camera means extract the position of the ground plane in the chosen reference and a serial of parameters, necessary to the following elaboration. These parameters are called intrinsics and they are:
- focal length (fo)
- image center (cc)
- radial distortion factor (k)
As told before, the goal of the camera calibration is to estimate the intrinsics parameters (focal length, image center and radial distortion factor) and to identify the position of the ground plane in the solidal reference with the camera.
Cameras calibration is a basic procedure to extract metric piece of information from 2D images. A camera is usually represented by the central projector model pinhole camera. This model is defined by two parameters:
- Intrinsic parameters (from three to five): they describe the camera independently from their position in the space.
- Extrinsic parameters (six): they describe camera position in the space, independently from their internal features.
This model must be conveniently correct to consider optical distortions introduced by camera lenses. The use of this kind of lenses, introduces a distortion which is necessary to balance before making a whatever calculation.
In literature there are several models to describe this kind of phenomenon. The model which has been studied and developed by Maestro 3D, estimates the lenses distortions in order to obtain a calibration which allows an excellent attention in the scanning process.
To calibrate a camera we could use the following way: focus on a chessboard whose dimensions are known, which is situated on the ground plane. From its examination, it is possible to obtain all the necessary piece of information.
How can I understand if my Scanner is not calibrated?
The main indicators of a non calibrated Scanner are clear disalignments on the surface, in the scanning process result.
In case of a bad calibration of the Scanner, it could be possible to see an error message of this type The object has moved during the Scanning process.
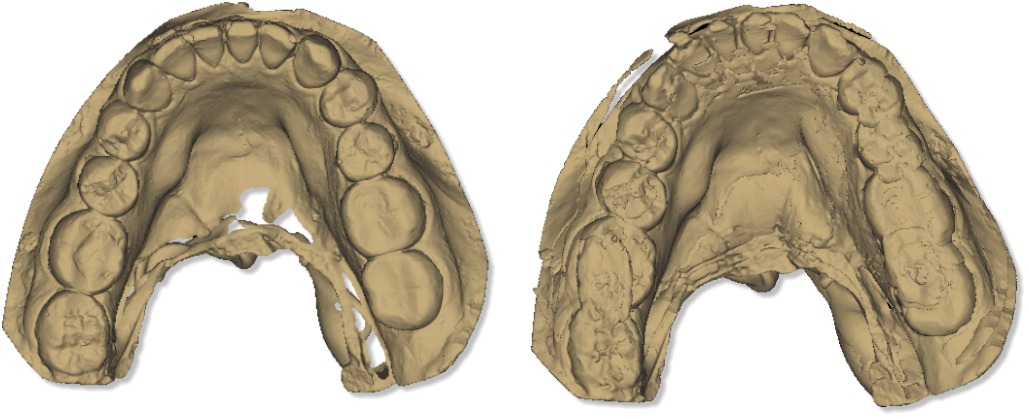
The picture here below, shows the same object, on the left we have a scan with a Scanner perfectly calibrated, while on the right a scan with a Scanner non-calibrated.
How many times it is necessary to calibrate the Scanner?
The quality of the materials and the solidity of the structure permit not to calibrate very often the Scanner if it has used correctly.
Nevertheless, excessive jump in the temperature or bad hits, could damage the machine and make the calibration necessary.
Small disalignments and imperfect calibrations are not evident on the final result, for this reason it is recommended to make the Scanner calibration every 1 month.
FAQ
How can I see the Software version and the scanner serial number?
From the menu of the main window, tap on the enter ? -> About.... The image below shows the About window of the Software. In this window there is the scanner serial number, (tap on the bottom to copy it in the clipboard) and the version number Build
- 1) Scanner serial number.
- 2) Copy scanner serial number into clipboard.
- 3) Software Build Release version.
How can I see if my Software version is updated to the last available?
From the main menu tap on the entry File -> Check for updates.
How can I know which modules are active?
From the main menu tap on the entry File and tap on the entry Activate for each available module. Here, a message that will show if the module is active will appear; otherwise a window to import the license file that will activate the module in case it is not, will open.
How can I make a backup of all the scans?
Just make a copy of the folder where the software saves all scans. By default the folder is c:\MaestroData\.
The software is very slow on startup, what can I do?
If the software is very slow on startup, the cause is probably that the save folder (by default c:\MaestroData\) contains many scans. Just empty the folder or delete it completely and restart the software.
How can I access the program settings?
Through the appropriate button shown in the figure you can access the settings screen.
With this screen you can change, language, skins, colors, display settings, scan settings and much more.
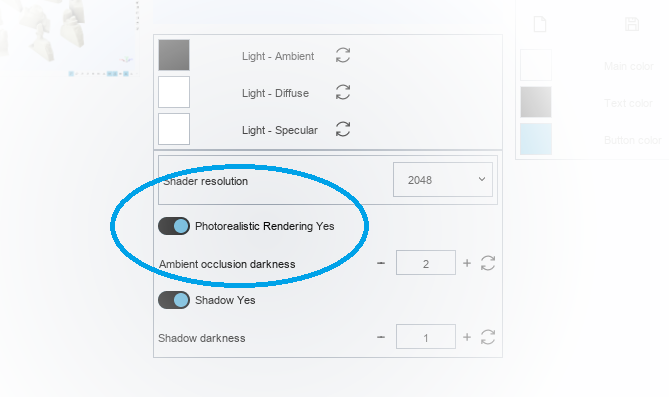
Photorealistic Rendering is very slow, how can I disable it?
Photorealistic rendering requires high performance video cards. We recommend using NVIDIA video cards, GeForce family, 10 GTX series or better with 2 GB RAM or more. To temporarily disable photorealistic rendering, press the appropriate button in the bottom toolbar as shown in the figure:
If you want to disable by default each time the software is started, it is advisable to disable it in the settings screen:
#How_can_I_access_the_program_settings.3F
Here you can disable photorealistic rendering:
How can I change the save folder?
Edit the file application.settings.xml which is located in the installation folder of the software and change the string MaestroFolderData="c://MaestroData". To restore the settings with default value, just delete the file application.settings.xml and restart the software.
Metal parts can be scanned?
Yes it's possible but in order to improve scanning of metal parts you must use a scanning spray. In the market there are a lot spray but we advise the [Vacalon quickcheck spray].
Why is the Maestro 3D scanner closed inside a chassis and not open like many others?
The choice to keep the scanner closed in a special chassis instead of leaving it completely open as is the current trend, is a choice dictated by our company philosophy. Maestro 3D follows a path of technological growth in which the goal is to obtain the best possible results, in terms of accuracy, precision, resolution and repeatability of the scanned 3D models.
The technology on which the Maestro 3D system is based is an advanced variant of structured light. This technology consists in projecting special light fringes on the object to be scanned. The cameras acquire hundreds of images in which the algorithms identify the passage of the luminous fringe from white to black. In other words, you should look for the edge of every single luminous fringe.
To do this and identify these edges with sub-pixel precision, a very high light contrast between white and black is needed. It is quite evident that having a scanner without a chassis, completely open, drastically reduces this contrast. Ambient light affects heavily reducing the contrast of the projected light. Less contrast means lower levels of accuracy and precision.
For this reason, Maestro 3D has decided to pursue the choice to enclose and protect the scanner from a closed chassis in order to eliminate any influence of ambient light.
Are the cameras in the scanner in color or are they monochrome? And why?
The cameras are monochromatic. This is because the algorithms that work with structured light or variants of this, must look the edge of each single light fringe. This is why we need a very high contrast between white and black. The grayscale image is obviously perfect for this purpose.
Working with color cameras would not help this recognition but would reduce the information held by the algorithm. This is because in the color cameras takes up space in the sensor to represent every single pixel with 3 channels (R,G,B), (Red, Green, Blue). With monochromatic cameras the same space is occupied only by the representation of the gray scale.
As the grayscale image is required to detect the edges of the light fringes, the monochrome camera collects much more useful data for the scanning process of a color camera.
If you decide to work with color cameras, it would still be necessary to convert the grayscale image via software to be able to scan. With the conversion you would lose a lot of information, obtaining a much less detailed grayscale image of the same grayscale image obtained from a camera with a native monochromatic sensor.
Why the Maestro 3D scanner is white light and not blue like many others?
The scanner cameras are monochrome in grayscale, therefore, the only effect that brings blue light is a lower contrast of the image.
By projecting white light the RGB channels of the projector sensor are used 100% because the white is obtained with (R=100%, G=100%, B=100%), this allows you to have high brightness and high contrast.
Using blue light or variations of it, the sensor channels of the projector are not used at 100%, example (R=0%, G=50%, B=100%). The only result obtained is a lower brightness and a lower contrast.
If the goal to be pursued is the highest precision, accuracy, resolution of a 3D scan, white light is better than blue light.
If the goal to be pursued is the effect on the audience and the scenography, blue light is probably better than white light.